Category: Articles
-

Green Technologies Shaping the Future of Renewable Fuels, Chemicals, Plastics, and Global Sustainability
Adopting green technologies for renewable fuels and chemicals can transform today’s challenging energy landscape into an advantage for all humanity by bypassing outdated fossil fuel infrastructures and leapfrogging into a sustainable future. Unlike traditional petrochemical industries that have long dominated developed markets, many regions of the world now have the chance to sidestep legacy systems…
-

Lignik – A Solution to Housing Issue
A feature story recently published in The Express Tribune newspaper highlights Lignik as a revolutionary solution for affordable, large-scale housing in Pakistan. Lignik is a groundbreaking, 3D-printable biosynthetic material derived from carbon dioxide and biowaste. Invented in Australia, this innovative material has the potential to revolutionise low-cost housing by offering a sustainable and affordable alternative…
-

Blue Mining – Sustainable Resource Extraction from the Ocean
The concept of blue mining, which involves the extraction of resources from ocean water and brine, is gaining momentum as a sustainable alternative to traditional terrestrial mining. Historically, seawater has been a source of essential minerals such as sea salt, magnesium, and bromine, with potassium often recovered from the residual bittern left after salt precipitation.…
-

Lignik Homes – A Sustainable Solution for Global Housing
As the world grapples with rapid urbanisation and pressing environmental challenges, innovative solutions for housing are more crucial than ever. Lignik Homes, constructed from the world’s first biosynthetic wood made from CO2, represent a groundbreaking approach to sustainable living. The Lignik Revolution Lignik is a revolutionary material that is 100% recyclable and produced from carbon…
-
Neurophology: Exploring the Interplay of Light and Photoacceptors in Brain Development
Neurophology is the study of the relationship between light and photoacceptor molecules in the body, as well as their impact on brain development and functioning. This field encompasses four distinct areas of science. The laws of quantum physics govern the absorption and desorption of light by photoacceptors, while the ensuing cascading reactions are dictated by…
-
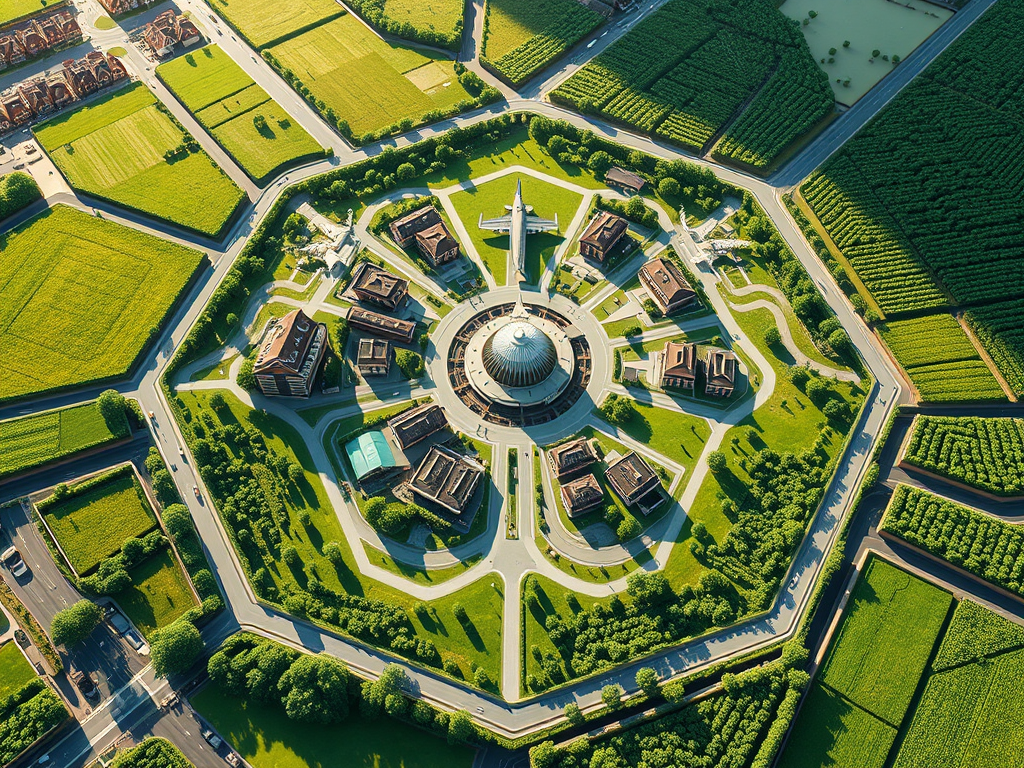

Hexa City – A Model for Sustainable Urban Development
In an era marked by rapid urbanisation and environmental challenges, the concept of an orycycle economy emerges as a beacon of hope for sustainable development. This model prioritises distributed manufacturing and recycling, fostering regional economies where locally consumed products are both produced and recycled within the community. Central to this vision is Hexa City, a…
-

Biogas Anaerobic Digestion: Processes, Technologies, and Industrial Applications
1 Introduction Biogas is naturally produced from the microbial decomposition of organic waste in an oxygen-free environment. Microorganisms consume the organic matter as a food source and release biogas as a waste product. This process, known as anaerobic digestion, is utilized in systems such as landfills, waste treatment plants, and dedicated biogas plants. These systems…
-
Solar Powered World: Calculating Land Requirements for a Global Baseload Demand
The answer is: 300,000 km² of land. We need a total of 300,000 km² (approximately 550 km x 550 km) of land to power the entire planet with solar panels. Currently, solar farms require 2 hectares (5 acres) of land per 1 MW solar farm. Newer solar panels have reduced this requirement to 1.3 hectares…
-
Regenerative Fuel Cell-Electrochemical Hydrogen Compressor Systems: The Future of Renewable Energy Storage
Hydrogen will be instrumental in the global shift towards an emission-free future. Fuel cells, being the most developed technology, are essential for its worldwide deployment. Their attractiveness is amplified by the growing surplus of electricity generated from renewable energy sources at both the residential and national levels. This surplus facilitates the broader adoption of fuel…
-

Beyond the Recycle Economy: Transitioning from Linear to Circular Bioeconomy
Take-make-forsake material flow model of the linear economies underpinned the twentieth century’s unprecedented industrialization and subsequent urbanization. While this model improved living standards, it consumed vast amounts of fossil fuels and natural resources, causing irreparable damage to the environment and climate. Now, a radical shift towards circular material flow chains is needed to decouple economic…